 number
of iterations: 1 2 3
number
of iterations: 1 2 3
Given an exisiting configuration
of the volumes. one selects a volume, which then will become the reference volume.
all the other volumes in the configuration are now interpretated as instances
of this reference volume, which has been moved and scaled in 3dspace.
so every instance consists the reference volume plus a transformation matrix
( translation, rotation, scaling ). this forms the axiom. every occurance of
the reference volume in the axiom is replaced by the axiom itself ( original
volume plus all transformed instances ). all these transformation matrixes are
further inherited to the next step during the process. the effect of this is
an amplification of the whole structure's deformations . this continuously repeated
process creates a perpetually growing geometry, but which still contains the
original parameters and transformations.
*
following example was generated using a standard cube with equal sides instead
of the central cube
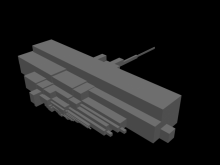 number
of iterations: 1 2 3
number
of iterations: 1 2 3
In the following example the left cube ( Haus
Wittgensteins dining room ) was selected as the reference volume .
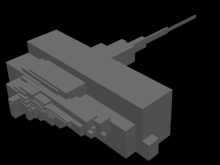 number
of iterations: 1 2 3
number
of iterations: 1 2 3
x1 ... xn transformation matrix ( translation, rotation, scale )
x1v-x2v-..-xnv
x1(x1v-x2v-..-xnv)- x2(x1v-x2v-..-xnv)-..- xn(x1v-x2v-..-xnv)
x1(x1(x1v-x2v-..-xnv)-x2(x1v-x2v-..xnv)-...-xn(x1v-x2v-..-xnv))- x2(x1(x1v-x2v-..-xnv)-x2(x1v-x2v-..xnv)-...-xn(x1v-x2v-..-xnv))-..- xn(x1(x1v-x2v-..-xnv)-x2(x1v-x2v-..xnv)-...-xn(x1v-x2v-..-xnv))